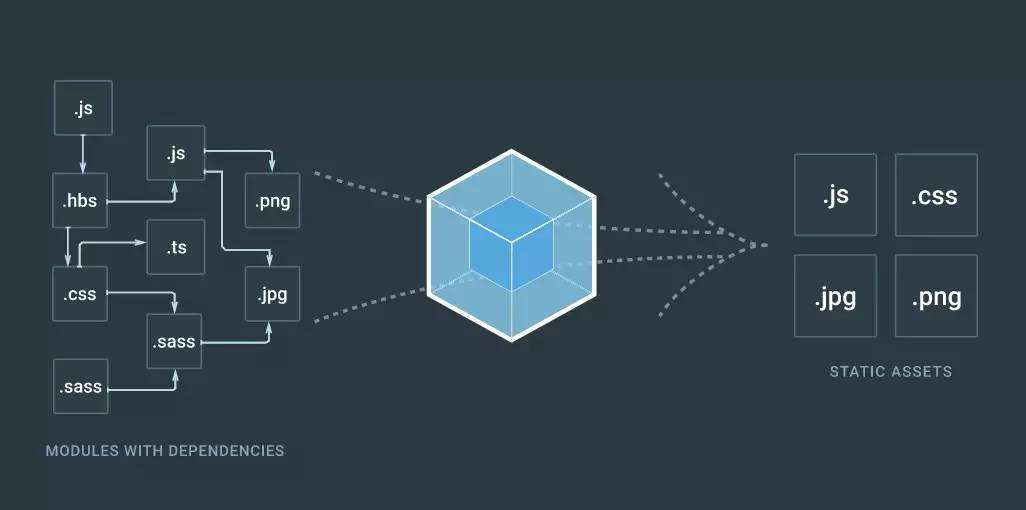
Webpack简介
Webpack是一个模块打包器 (module bundler),能够将任何资源如 JavaScript 文件、CSS 文件、图片等打包成一个或少数文件。
如果没有模块打包工具,我们就得在HTML中加载无数script标签了,这样的缺点显而易见,我们得关心文件的加载顺序和依赖关系,多个script标签也意外着多余的网络请求等等。
而Webpack就是为了解决这些问题而生的。
Webpack最新版本为v3,我这里就用的webapck3。如果之前用的是v1,可以阅读官方的v1迁移到v2,而v2和v3差别不大。
安装
依赖
安装Webpack前得先安装好Nodejs和npm
安装方式
Webpack安装分为全局安装和本地安装
全局安装虽然使用很方便,但它不会包括在项目的依赖模块列表中。
更规范化的操作是使用本地安装CLI包,然后用相对路径或是npm脚本中运行它。
本地安装
先用npm init 一路回车来创建一个项目,得到package.json
然后
1
| npm install webpack --save-dev --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
安装webpack,我这里使用了淘宝镜像
为方便后面实例,再安装个lodash:
1
| npm install lodash --save --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
使用Webpack
npm scripts中使用
首先创建src目录和index.js文件
1
2
| mkdir src && cd src
vim index.js
|
index.js内容很简单,简单输入数组中各个数的平方,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| var _ = require('lodash');
console.log(_.map([1,2,3,4,5,6], function(n) {
return n*n;
})
);
|
备注,关于这里的lodash模块引用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| // 这里引用lodash有两种方式,分别如下:
var _ = require('lodash')
import _ from 'lodash'
// 这里两种方式在webpack中都能工作
// 只是第一种是常见在nodejs开发中,是commonJs规范的一部分
// 第二种属于ES6中新的模块化加载规范
|
然后回到项目根目录,编辑package.json文件的scripts部分,新增build命令,如下:
1
2
3
| "scripts": {
"build": "webpack src/index.js dist/bundle.js",
}
|
然后
就会生成dist/bundle.js,使用
就会运行该文件,也可以使用html将其跑在浏览器端。
使用Webpack配置文件
上面的的实例我们是使用webpack命令行,但是如果使用更多的功能,我们就得使用webpack的配置文件
一般的,我们会在项目根目录下创建一个配置文件:webpack.config.js,Webapck会默认寻找该文件,使用–config [filename]可以指定一个配置文件。
我们来使用配置文件做上一个命令行中的事,新建webpack.config.js,内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
}
};
|
package.json中的build只用写webpack:
然后:
依然会像命令行一样成功打包。
更专业一点
打包前我们需要先删除dist目录,这里使用del-cli工具,可以不用顾虑操作系统差别。
1
| npm install del-cli --save-dev --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
接着更新package.json中npm脚本如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| "scripts": {
"prebuild": "del-cli dist -f", // 删除目录
"build": "webpack",
"execute": "node dist/bundle.js", // 运行打包出来的文件
"start": "npm run build -s && npm run execute -s" // 打包
}
|
这样我们使用起来就很方便了。
Webpack加载器 Loaders
加载器可以提前帮我们转换或操作特定类型的文件,比如通过Babel加载器把ES6转为ES5,打包Css文件图片等等都会用到loader。
这里我们以用Babel把ES6转为ES5为例,首先把刚才的index.js改为ES6写法。
vim index.js:
1
2
3
| import _ from 'lodash';
console.log(_.map([1,2,3,4,5,6], n => n*n));
|
安装依赖的包:
1
| npm i -D babel-core babel-loader babel-preset-es2015 --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
然后新建.babelrc文件,内容如下:
1
2
3
| {
"presets": ["es2015"]
}
|
编辑webapck.config.js文件如下(新增module):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
}
};
|
然后执行:
loader的作用很大,常见还有style-loader,file-loader等等。这个大家可以在实践中发掘。
插件
Loader和Plugins的不同
Loader主要在加载两字,是用于预处理文件的。而插件一般是用来增强Webpack功能的
使用插件
这里只用CleanWebpackPlugin插件举一个简单例子,CleanWebpackPlugin用来删除目录的(和我们上面的del-cli功能差不多)
安装包:
1
| npm install clean-webpack-plugin --save-dev --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
编辑webapck.config.js文件如下(新增plugins):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist'])
]
};
|
然后使用
这里只是简单讲下plugins用法,Webpack还有许多有用的插件
多文件打包
上述例子只是只有一个输入文件index.js,一个输出文件bundle.js,假如我们有多个文件分别打包怎么办呢?
写法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: {
index: './src/index.js',
app: './src/app.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
}
};
|
这样就可以通过入口文件动态生成bundle文件。
开发环境
webpack提供许多供开发时使用的功能,下面简单介绍下:
代码映射(Source map)
Webpack在打包后如果发生错误,很难定位到,Source map就是解决这个问题的,它可以把编译后的代码映射回原始源码,便于我们定位错误。Webpack提供了十种风格的代码映射,具体见:官方手册devtool,这里我们以inline-source-map为例。
启用Source map很简单,就是module.exports中新增devtool属性,然后指定映射风格。如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist'])
]
};
|
这样我们在打包时便能很清楚的在控制台上看到相应错误。
Webpack-dev-server插件
Webpack-dev-server提供了一个简单的服务器环境,并提供实时加载代码功能。
先安装包:
1
| npm install webpack-dev-server --save-dev --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
启用只需配置文件中设置devServer,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist'])
]
};
|
新增npm scripts,增加一条run-server命令,编辑package.json:
1
| "start:dev": "webpack-dev-server --open"
|
然后运行:
浏览器就会自动加载应用的页面默认在:localhost:8080显示,当然也可以通过在devServer设置类似port: 9000指定端口,更多设置请查看官方文档手册。
生产环境
命令行执行webpack -p 时就会构建生产环境应用,它会完成以下步骤:
- 使用 UglifyJsPlugin (webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin) 压缩 JS 文件 (此插件和 uglifyjs-webpack-plugin 相同)
- 运行 LoaderOptionsPlugin 插件,这个插件是用来迁移的,见 document
- 设置 NodeJS 的环境变量,触发某些 package 包以不同方式编译
在配置文件中使用process.env.NODE_ENV环境变量
Webpack -p 相当于 webpack –optimize-minimize –define process.env.NODE_ENV=”‘production’”,但是在Webpack配置文件无法读取process.env.NODE_ENV环境变量
这里我们可以使用cross-env包:
1
| npm install --save-dev cross-env --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
设置package.json的build为生产版本
1
| "build": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack -p",
|
现在可以在配置文件中使用process.env.NODE_ENV了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '[name].[chunkhash].js' : '[name].bundle.js' // 根据环境为文件命名
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist'])
]
};
|
多配置文件配置
在常规开发中,我们一般会为开发环境和生产环境设置不同的配置文件。这里我们先一个基本文件,包含所有环境都包含的配置,然后使用webapck-merge将它和特定环境的配置文件合并并导出。
首先安装webpack-merge:
1
| npm install --save-dev webpack-merge --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
|
webpack.common.js:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist'])
]
};
|
webpack.dev.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const Merge = require('webpack-merge');
const CommonConfig = require('./webpack.common.js');
module.exports = Merge(CommonConfig, {
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
output: {
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify('development')
}),
new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin()
]
});
|
webpack.prod.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| const webpack = require('webpack');
const Merge = require('webpack-merge');
const CommonConfig = require('./webpack.common.js');
module.exports = Merge(CommonConfig, {
devtool: 'cheap-module-source-map',
output: {
filename: '[name].[chunkhash].js'
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify('production')
}),
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin()
]
});
|
然后在package.json中新增build:dev和build:prod scripts:
1
2
| "build:dev": "webpack-dev-server --open --config webpack.dev.js",
"build:prod": "webpack --progress --config webpack.prod.js"
|
现在只需执行npm run build:dev或npm run build:prod便可以得到开发版或者生产版了
代码分离
举个例子,比如我们有两个js文件,都引入了lodash,在打包时这两个入口文件都会引入lodash,这很大程度上造成了冗余,在同一个页面我们只需引入一个lodash就可以了。
我们可以使用CommonChunkPlugin插件来将相同部分提取出来放到一个单独模块中。
为达到演示效果,新增一个src/test.js:
1
2
3
4
5
| const _ = require('lodash');
var str = _.join(['a', 'b', 'c']);
console.log(str);
|
编辑webpack.config.js:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| const webpack = require('webpack');
const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
entry: {
index: './src/index.js',
test: './src/test.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: 'webpack demo',
filename: 'index.html'
}),
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist']),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'common' // 抽取出的模块的模块名
}),
]
};
|
这样就会打包出公共的common.bundle.js和各自的index.bundle.js和test.bundle.js文件。
懒加载(Lazy loading)
我们可以使用import()来实现懒加载,在需要的时候才加载相应的模块,减少应用初始化时加载暂不需要的模块的压力,提高程序运行速度。
编辑src/hello.js
1
2
3
4
5
| console.log("The hello.js module has loaded!");
export default function hello() {
console.log('hello');
}
|
编辑src/say.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| const btn = document.getElementById(".clickMe");
btn.onclick = function() {
import(/* webpackChunkName: "hello" */ './hello').then(function(module) {
var hello = module.default;
hello();
});
};
|
编辑webpack.config.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| const path = require('path');
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
devtool: 'inline-source-map',
devServer: {
contentBase: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')
},
entry: {
say: './src/say.js',
hello: './src/hello.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].bundle.js',
chunkFilename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: 'webpack demo',
filename: 'index.html'
}),
new CleanWebpackPlugin(['dist'])
]
};
|
打包后新建一个html文件,包含一个id为clickMe的button,然后运行html,点击按钮。就会看到效果。
好了,webpack的总结就到这里了,这个只是大致入门了解,更多的还需要过一遍官方文档,然后结合实际项目才能使用好webpack。